Understanding the rise of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) levels is a critical aspect for those monitoring early pregnancy or navigating fertility treatments. Often referred to as the pregnancy hormone, HCG serves a key role in sustaining early pregnancy by supporting progesterone production and stabilizing the uterine lining. It provides essential clues about implantation success, which is pivotal in assessing pregnancy progression. Let’s delve deeper into the timeline, factors, and conditions that influence the rise of HCG levels after implantation, answering common questions like “How long after implantation does HCG rise?” and “How soon after implantation is HCG detectable in blood or urine?”
What Is HCG and Its Role?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) is an essential hormone produced by the trophoblast cells surrounding a developing embryo shortly after implantation. This hormone serves a dual purpose: it helps maintain the uterine lining by stimulating progesterone production and ensures the embryo has a stable environment for growth. Detectable in both blood and urine, HCG plays a pivotal role in early pregnancy. It signals the body to halt menstruation, marking the initial stages of pregnancy and supporting the continuation of gestation. Additionally, HCG levels provide vital insights into implantation success and pregnancy progression, answering critical questions like “when does HCG rise after implantation?” and “how quickly does HCG increase in blood and urine?” The hormone’s role extends to sustaining pregnancy health, making its monitoring indispensable for those undergoing natural conception or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
Which embryonic structure produces HCG?
HCG is produced by the trophoblast, a vital component of the developing embryo that eventually forms the placenta, playing a crucial role in the pregnancy’s progression. This early production of HCG signifies a key milestone, as it ensures the embryo’s ability to signal the body to support the uterine lining and prevent menstruation. The hormone’s production starts shortly after implantation and helps maintain the necessary hormonal balance required for a healthy pregnancy. By stabilizing progesterone levels and fostering a nurturing environment, HCG enables the embryo to thrive. Questions such as “when does HCG rise after implantation?” and “how quickly does HCG become detectable in tests?” often revolve around this essential phase of development, underscoring its significance in early pregnancy health.
How Long After Implantation Does HCG Rise?
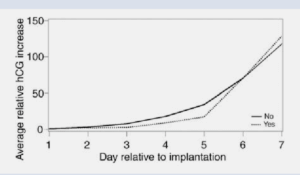
HCG typically starts rising within 24 to 48 hours after implantation. This rise is gradual at first but becomes exponential over the following days. Understanding this timeline helps answer questions like:
- How soon after implantation does HCG rise?
- When does HCG start to rise after implantation?
- How quickly does HCG rise after implantation?
HCG Levels in Urine and Blood
While blood tests can detect HCG levels as early as 1-2 days after implantation, urine tests may take longer, typically requiring 4-5 days to show detectable levels. This delay explains why early pregnancy tests might yield faint lines initially.
Factors Influencing HCG Levels
Implantation Timing
Late implantation can lead to lower initial HCG levels. Questions like “can late implantation cause low HCG levels?” and “does HCG rise after late implantation?” are common. The answer lies in the timing and efficiency of implantation.
Type of Pregnancy
- Twins or Multiples: Twin pregnancies often exhibit higher HCG levels. For example:
- HCG levels at 4 weeks in twins are generally higher than in single pregnancies.
- HCG levels at 6 weeks in twins can significantly exceed normal ranges.
- Ectopic or Molar Pregnancies: Abnormally high or low HCG levels can indicate complications like ectopic pregnancy or molar pregnancy.
Individual Variations
Some women experience a slow HCG rise without any complications, while others may have fluctuating progesterone and HCG levels, affecting test outcomes.
When Does HCG Peak?
HCG levels peak around 8–11 weeks of pregnancy. After this point, they begin to decline and stabilize. This pattern is crucial for monitoring pregnancy health and answering questions like:
- When does HCG level off?
- Does HCG stop doubling every 48 hours?
HCG Levels During Implantation Bleeding
Implantation bleeding is a common early pregnancy symptom. During this phase, HCG levels start to rise but may not yet be detectable in urine. It’s vital to consider that:
- HCG levels during implantation bleeding are often too low for home pregnancy tests.
- When does HCG rise after implantation bleeding? Detection typically occurs within 3-4 days post-bleeding.
How Fast Does HCG Rise After Implantation?
Doubling Time
HCG levels double approximately every 48 to 72 hours in the early stages of pregnancy, providing a critical benchmark for tracking and assessing pregnancy progression. This rapid escalation of HCG not only signifies healthy implantation but also aids in predicting pregnancy milestones. For instance, questions like “How quickly after implantation does HCG rise?” or “How does HCG level progression indicate fetal health?” can be better understood through this doubling timeline. Utilizing tools such as an HCG calculator allows individuals to estimate their pregnancy timeline more precisely by interpreting beta levels, offering reassurance during this crucial phase. Additionally, understanding how HCG interacts with other factors, such as progesterone or implantation timing, enhances clarity about early pregnancy dynamics.
Late Implantation and HCG
Late implantation might delay HCG detection, leading to queries like “does late implantation cause low HCG?” While late implantation can result in slower initial rises, the hormone’s doubling rate often aligns with standard pregnancy expectations.
Buy Now for Early Pregnancy Monitoring Tools
Tracking HCG levels is essential for early pregnancy health. Explore our range of HCG testing kits and calculators to monitor your journey. Buy Now to ensure accurate and timely results for your peace of mind.
HCG Levels After IVF Implantation
For those undergoing IVF, the timeline of HCG rise is slightly different. Questions like how long after IVF implantation does HCG rise? And what is beta testing in IVF? are common. Typically:
- Blood tests for HCG, called beta tests, are conducted 9–14 days post-transfer.
- Low beta HCG levels in IVF might indicate delayed implantation or other concerns.
HCG Levels and Miscarriage Risk
Slowly Rising HCG Levels
While a slow HCG rise can indicate complications, it doesn’t always signal miscarriage. Monitoring doubling rates over several days provides better insights.
High HCG Levels
Extremely high levels may suggest multiple pregnancies, molar pregnancies, or other abnormalities. Always consult a healthcare provider for interpretation.
HCG and Progesterone Interaction
Progesterone supports pregnancy alongside HCG. Questions like does taking progesterone increase HCG levels? arise frequently. While progesterone doesn’t directly influence HCG, both work together to maintain a healthy pregnancy environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long After Implantation Is HCG Detectable?
HCG can be detected in blood within 1-2 days post-implantation and in urine after 4-5 days. However, factors like hydration levels and test sensitivity can affect detection timing.
Does HCG Rise Before Implantation?
No, HCG production begins only after the embryo implants into the uterine lining. Pre-implantation HCG levels remain negligible.
Why Is HCG Higher in the Morning?
Morning urine is more concentrated, leading to higher HCG detection levels. This is why early morning is recommended for pregnancy testing.
How long after implantation will you test positive?
You can test positive approximately 4-5 days after implantation using a urine test, while blood tests may detect HCG as early as 1-2 days post-implantation.
What are signs your hCG is rising?
Signs include a positive pregnancy test, early pregnancy symptoms like nausea, fatigue, and breast tenderness, and confirmation through blood tests.
How long after implantation does it take for hCG to be detectable?
HCG becomes detectable in blood 1-2 days after implantation and in urine 4-5 days after implantation.
How soon after IVF implantation can I test?
For IVF pregnancies, blood tests (beta tests) are typically conducted 9–14 days post-embryo transfer.
What is the hCG level at 1 week?
At 1 week post-implantation, HCG levels are usually between 5 and 50 mIU/mL.
How do I know if implantation is successful?
Successful implantation is indicated by a positive pregnancy test, rising HCG levels, and early pregnancy symptoms.
Conclusion
Understanding the timeline and factors influencing HCG rise after implantation is vital for early pregnancy monitoring. Whether you’re navigating natural conception or IVF, knowing when and how HCG levels rise can provide reassurance and clarity. For accurate tracking, consider using reliable testing tools and consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.